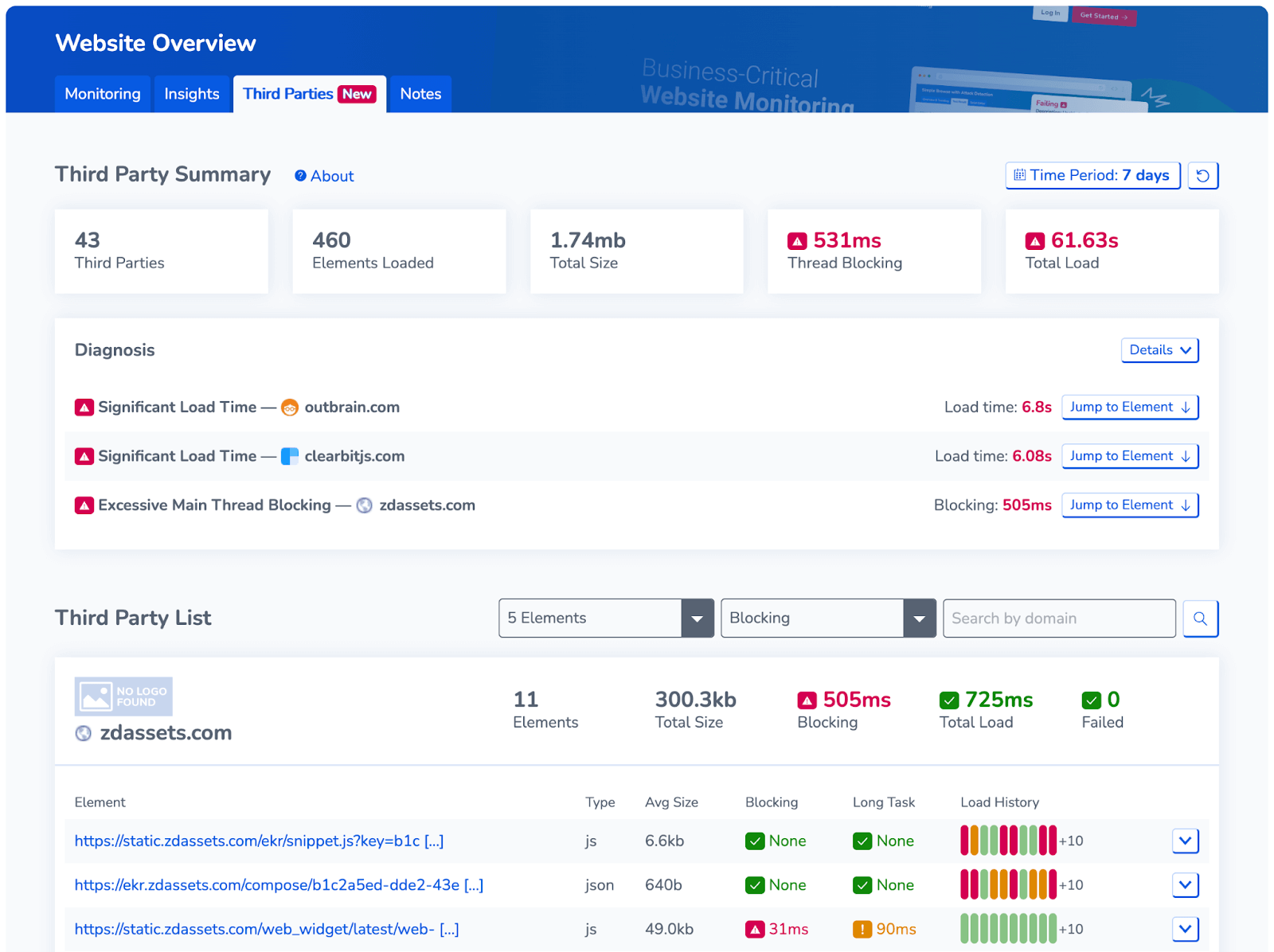
Every single day RapidSpike detects thousands of problems with website third-party plugins that are causing revenue and customer experience issues, and 90% of them are not just affecting our users; they are affecting every user of that third party. The difference is with RapidSpike, we tell them about it.
In 2018, a major e-commerce website experienced a significant performance failure due to a third-party plugin. The website had implemented a third-party plugin to manage its shopping cart and checkout process. However, after a recent update to the plugin, the website’s performance began to suffer.
The website’s page load times slowed considerably, leading to a significant increase in bounce rates and a decrease in revenue. RapidSpike soon discovered that the third-party plugin was causing the problem, as it was making many server requests that took too long to complete.
To address the issue, the development team quickly rolled back the plugin to a previous version and began working with the plugin’s vendor to resolve the issue. After several weeks of collaboration, the vendor was able to release a new version of the plugin that determined the performance issues.
Although the issue was eventually resolved, the website’s owners were left with a valuable lesson learned about the importance of carefully evaluating and testing third-party plugins before implementing them on a website.
What is a website third-party plugin?
A website third-party plugin is a software component that can be added to a website to add new features or functionality that is not part of the website’s core technology stack. Third-party plugins are typically developed by third-party vendors and can be integrated into a website by adding code snippets or installing software packages.
Third-party plugins can serve a wide range of purposes on a website, such as adding social media sharing buttons, implementing contact forms, providing e-commerce functionality, or integrating analytics tools. Some plugins are free to use, while others require a subscription or a one-time purchase fee.
When should third-party be used?
While third-party plugins can add significant value to a website, it is vital to be cautious when using them. Poorly developed or maintained plugins can create security vulnerabilities or cause website performance issues. It is essential to carefully evaluate third-party plugins’ security, performance, compatibility, reliability, and support before implementing them on a website.
Third-party plugins can be helpful to websites for several reasons:
- Increased functionality: Third-parties can add new features and functionality to a website that may not be available through the website’s core technology stack.
- Customisation: Plugins can allow for customisation of a website’s design and user experience.
- Time-saving: Third-party plugins can save time for website developers by providing pre-built solutions for common website needs.
- Cost-effective: Similarly, plugins can be cost-effective compared to developing custom solutions in-house.
- Innovation: Third-party plugins can provide access to new and innovative technologies.
What threats do plugins pose to a website?
Overall, third-party plugins can provide significant benefits for websites. However, it is crucial to carefully evaluate the security, performance, compatibility, reliability, and support of third-party plugins before implementing them on a website to avoid potential issues such as:
- Security: Third-parties can create security vulnerabilities on the e-commerce website, leading to data breaches and other cyber threats.
- Performance: Third-party plugins can slow down the website’s performance, leading to a poor user experience and lost sales.
- Compatibility: Plugins may not be compatible with the e-commerce website’s technology stack, which can cause technical issues and downtime.
- Reliability: Third-parties may not be reliable, which can cause website downtime and lost sales.
- Support: E-commerce companies may not get adequate support from third-party plugin providers, which can lead to technical issues and lost sales.
Who is responsible for third-parties?
The business owner is responsible for ensuring nothing on their site is causing an issue, even a third. It is often difficult to track problems that are happening with third-parties. They can be hidden for many months before the problems are discovered. Sometimes the third-party knows about the issue, but sometimes they have no idea that something is broken.
Whilst third-party website plugins can benefit e-commerce companies such as increased functionality and customisation, they also pose potential challenges that need to be managed effectively.
E-commerce companies should carefully evaluate the security, performance, compatibility, reliability, and support of third-party website plugins before implementing them on their website.
RapidSpike is explicitly designed to help with the overall e-commerce store management. Ensure website performance, security, and reliability of your third-parties are tracked, alerted on and managed, so you can react to the problems quickly and effectively.
Third-party horror stories happen every day, from website takedowns to horrendous performances to hacking. Don’t let your website be next. Do you know who is misbehaving on your website? Find out today with a 30-day free trial of RapidSpike.
RapidSpike Third-Parties Explorer






